Understanding the Need for AI Orchestration Frameworks
The rise of agentic AI has created a new challenge:
LLMs are powerful at reasoning but unreliable at coordinating multi-step workflows, handling tools, managing state, or collaborating with other agents.
By default, LLMs struggle to:
- Manage tool sequences
- Run long or interruptible workflows
- Preserve state across steps
- Coordinate multiple agents
- Maintain deterministic control flow
- Interact with APIs consistently
- Handle retries, logging, and error recovery
This is why AI orchestration frameworks have become the backbone of modern agentic systems.
These frameworks—LangGraph, Semantic Kernel, CrewAI, and LlamaIndex—provide the missing infrastructure layer that helps AI systems behave like real software: stateful, predictable, traceable, multi-step, and production-safe.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- How each orchestration framework works
- Key differences between LangGraph, Semantic Kernel, CrewAI, LlamaIndex
- Their real use cases, strengths, and weaknesses
- When to choose each framework
- Architecture diagrams, examples, and comparison tables
This is your Tier-2 authoritative guide, built for developers, architects, AI engineers, and search engines.
What Are AI Orchestration Frameworks?
AI orchestration frameworks are systems that coordinate how LLMs:
- Think
- Plan
- Act
- Use tools
- Maintain state
- Recover from failures
- Execute workflows
- Interact with memory
- Work with other agents
They transform LLMs from single-shot text generators into structured, reliable, multi-step autonomous systems.
In short:
LLMs = brains
Orchestration frameworks = nervous system
Why LLMs Need Orchestration (Core Problems They Solve)
Problem 1 — LLMs forget previous steps
→ Framework solution: persistent state machines
Problem 2 — Tools must be sequenced correctly
→ Framework solution: DAGs, graphs, planners
Problem 3 — Agents fail silently
→ Framework solution: guardrails, retries, error paths
Problem 4 — Multi-agent collaboration is chaotic
→ Framework solution: supervisors, message-routing
Problem 5 — Outputs are inconsistent
→ Framework solution: structured outputs, function calling
Problem 6 — Tasks time out
→ Framework solution: checkpoints + resumability
This is why orchestration frameworks are essential for production systems.
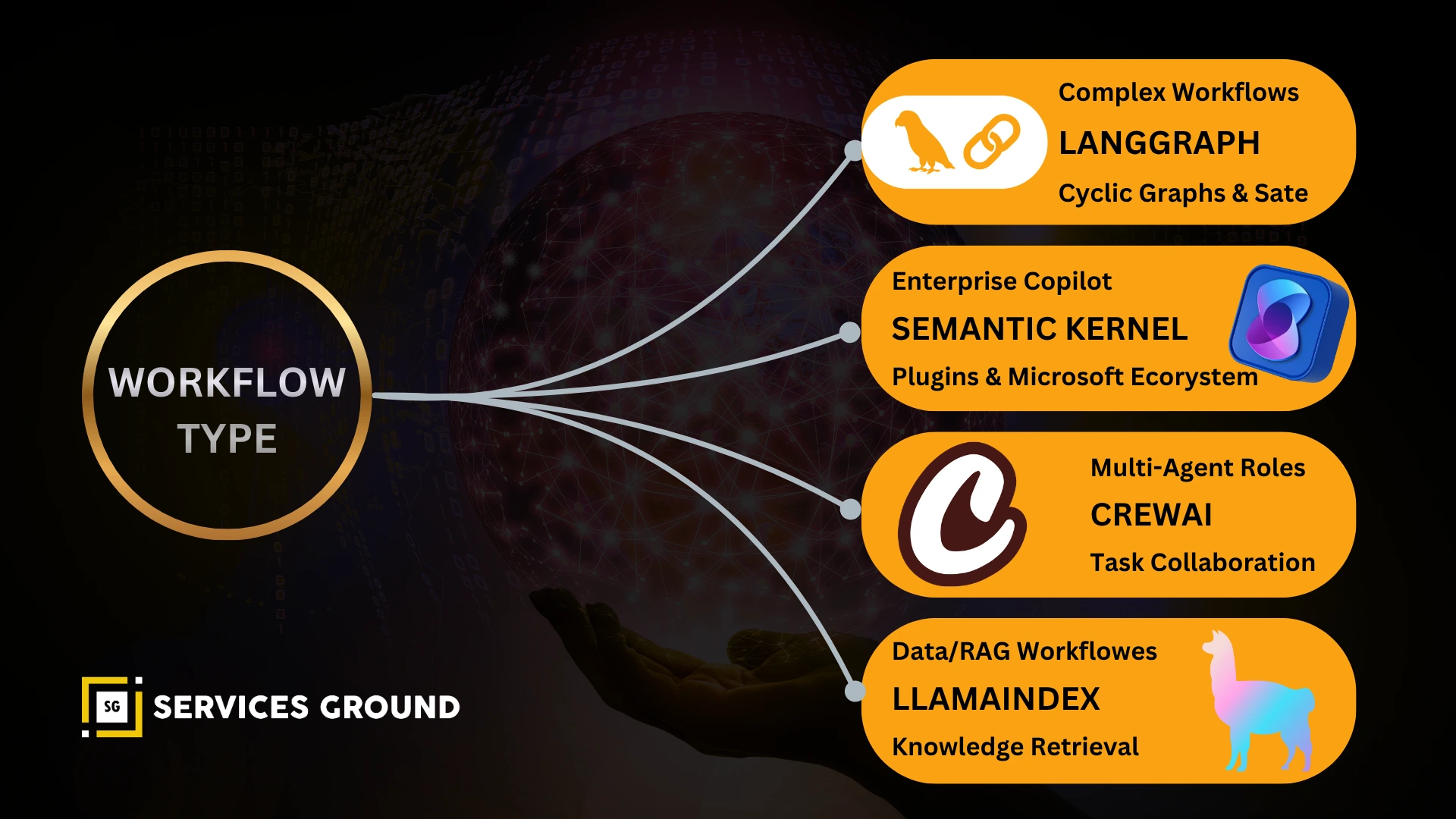
The Top AI Orchestration Frameworks in 2025
This guide focuses on the four dominant frameworks shaping agentic AI today.
LangGraph — Graph-Based, Stateful AI Workflows
LangGraph (by LangChain) is the leading framework for building stateful graph workflows driven by LLMs.
It uses nodes, edges, and predictable state flows to execute complex agentic pipelines.
Key Capabilities
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Deterministic graph control flow | Predictable, observable workflows |
| Persistent state | Stores memory at every node |
| Checkpoints | Resume from any state |
| Multi-agent graphs | Supervisors, subgraphs |
| Tool calling | Native support |
| Human-in-the-loop | Interrupt and resume |
Example Workflow (Real LangGraph Code)
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph def analyze(state): state["analysis"] = "Initial assessment completed." return state def finalize(state): state["result"] = f"Final summary based on: {state['analysis']}" return state graph = StateGraph() graph.add_node("analysis", analyze) graph.add_node("finalize", finalize) graph.set_entry_point("analysis") graph.add_edge("analysis", "finalize") app = graph.compile() response = app.invoke({"input": "Start workflow"}) print(response)
Strengths & Weaknesses
Strengths
- Best for complex, multi-step agent workflows
- High observability (flow visualization + logs)
- Powerful for multi-agent systems
Weaknesses
- Steep learning curve
More engineering than prompt-engineering
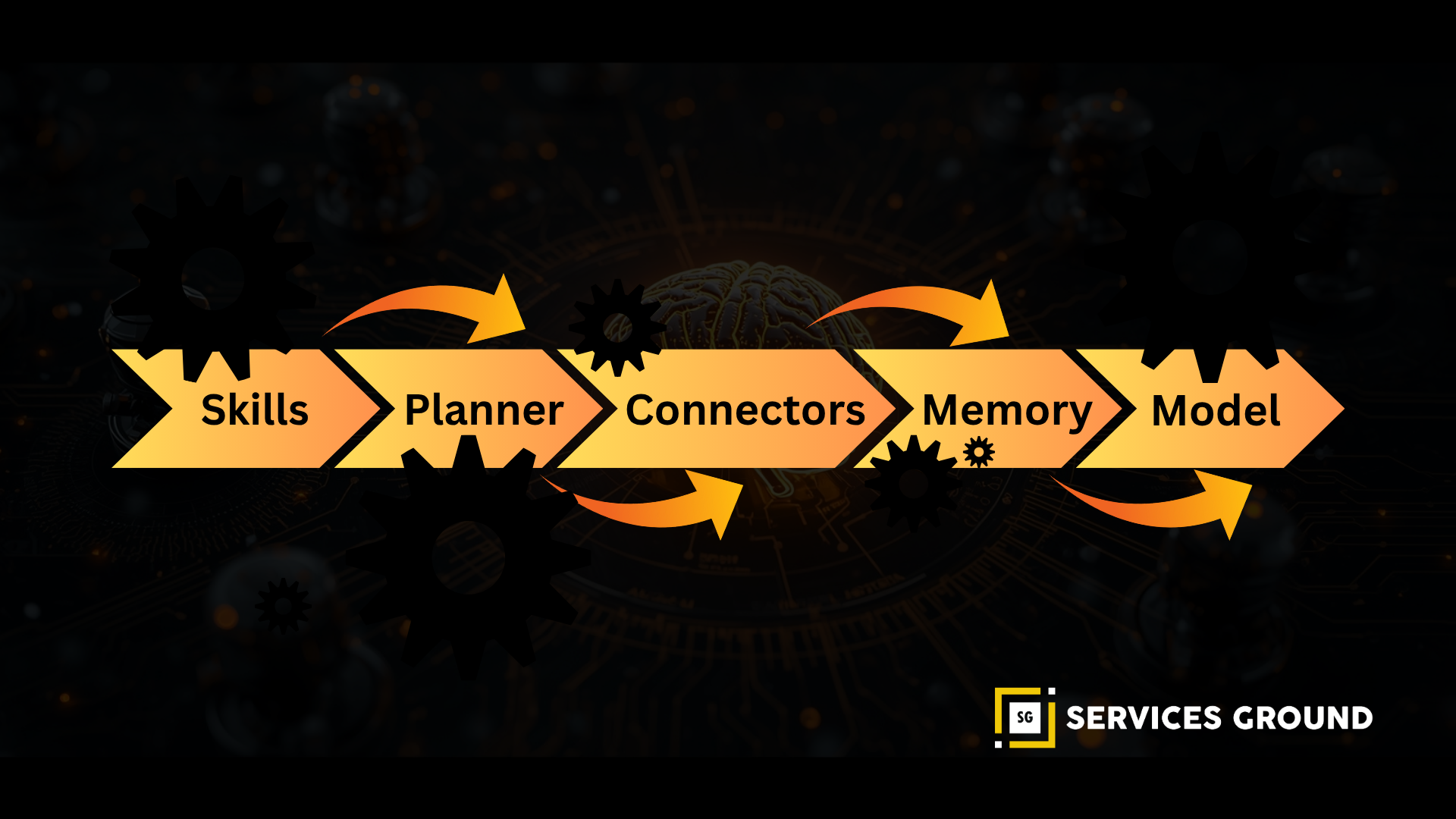
Semantic Kernel — Enterprise-Grade AI Orchestration
Semantic Kernel (Microsoft) is designed for enterprise orchestration with:
- Planners
- Skills
- Policies
- Connectors
- Memory plugins
It integrates deeply with Azure, compliance requirements, and cloud workloads.
Key Capabilities
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Skills system | Functions as modular AI abilities |
| Planners | Auto-generate workflows |
| Policy enforcement | Governance + safety |
| Enterprise integrations | Azure, Microsoft 365 |
| Memory plugins | SQL, Cosmos, vector DBs |
Real Semantic Kernel Example
import semantic_kernel as sk kernel = sk.Kernel() @kernel.function def summarize(text: str): return text[:100] + "..." response = kernel.invoke("summarize", text="AI orchestration frameworks structure agent actions.") print(response)
Strengths & Weaknesses
Strengths
- Best enterprise governance
- Azure-first architecture
- Balanced AI + app orchestration
Weaknesses
- Not ideal for branching agentic reasoning
Fewer multi-agent abstractions
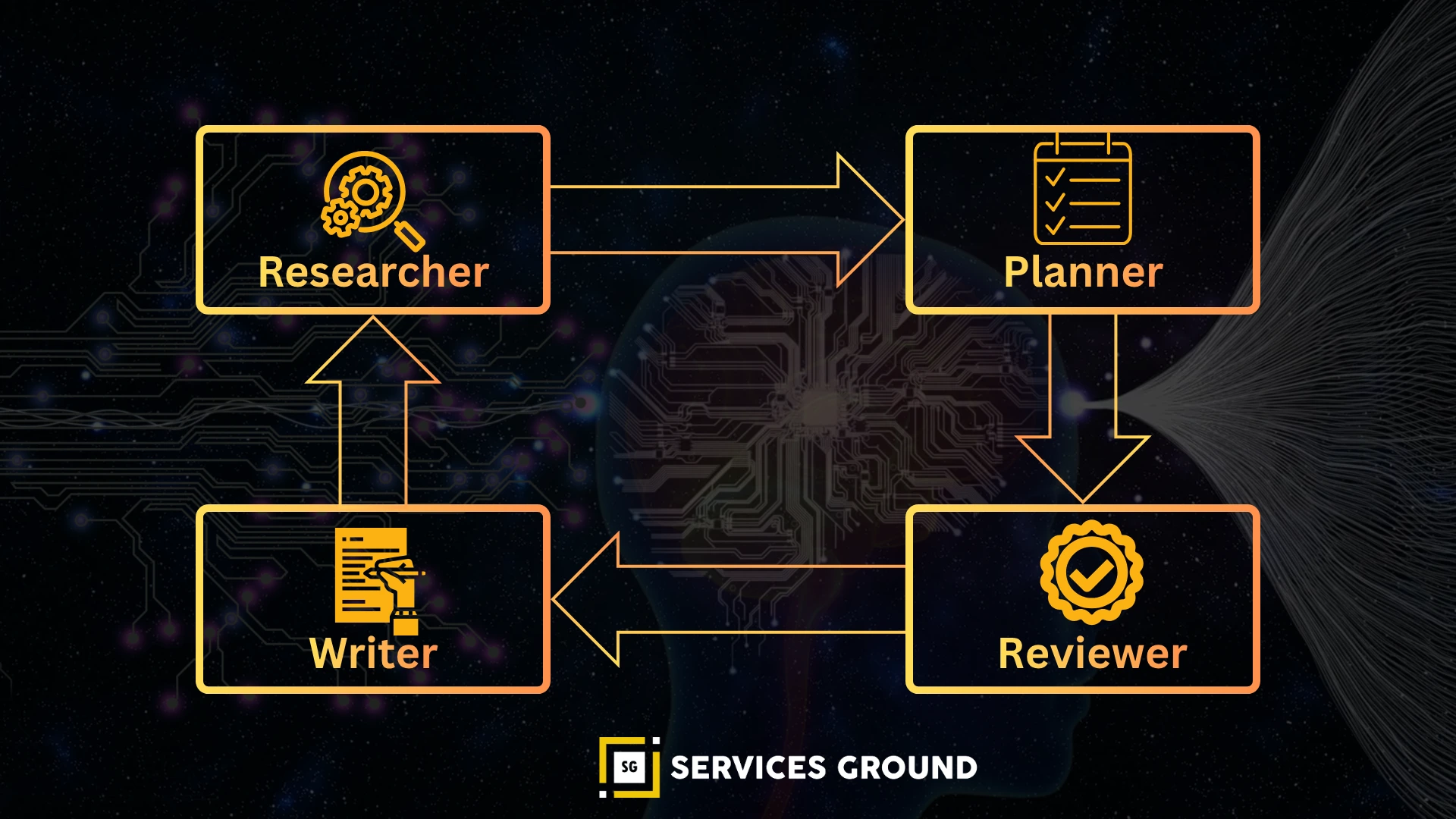
CrewAI — Role-Based Multi-Agent Teams
CrewAI models agents as roles, similar to human teams:
- Researcher
- Planner
- Coder
- Writer
- Reviewer
Each agent has tools and responsibilities.
Key Capabilities
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Role-based agents | Natural human-like collaboration |
| Sequential & parallel tasks | Flexible multi-agent execution |
| Agent-to-agent messaging | Coordination |
| Easy setup | Beginner-friendly |
CrewAI Example
from crewai import Agent, Crew, Task researcher = Agent(role="Researcher", goal="Collect orchestration insights.") writer = Agent(role="Writer", goal="Create a clear explanation.") task1 = Task(agent=researcher, description="Research frameworks.") task2 = Task(agent=writer, description="Write structured summary.") crew = Crew(agents=[researcher, writer], tasks=[task1, task2]) print(crew.run())
Strengths & Weaknesses
Strengths
- Best for simple multi-agent workflows
- Very human-friendly mental model
Weaknesses
- Not designed for enterprise-grade orchestration
- Less control compared to LangGraph
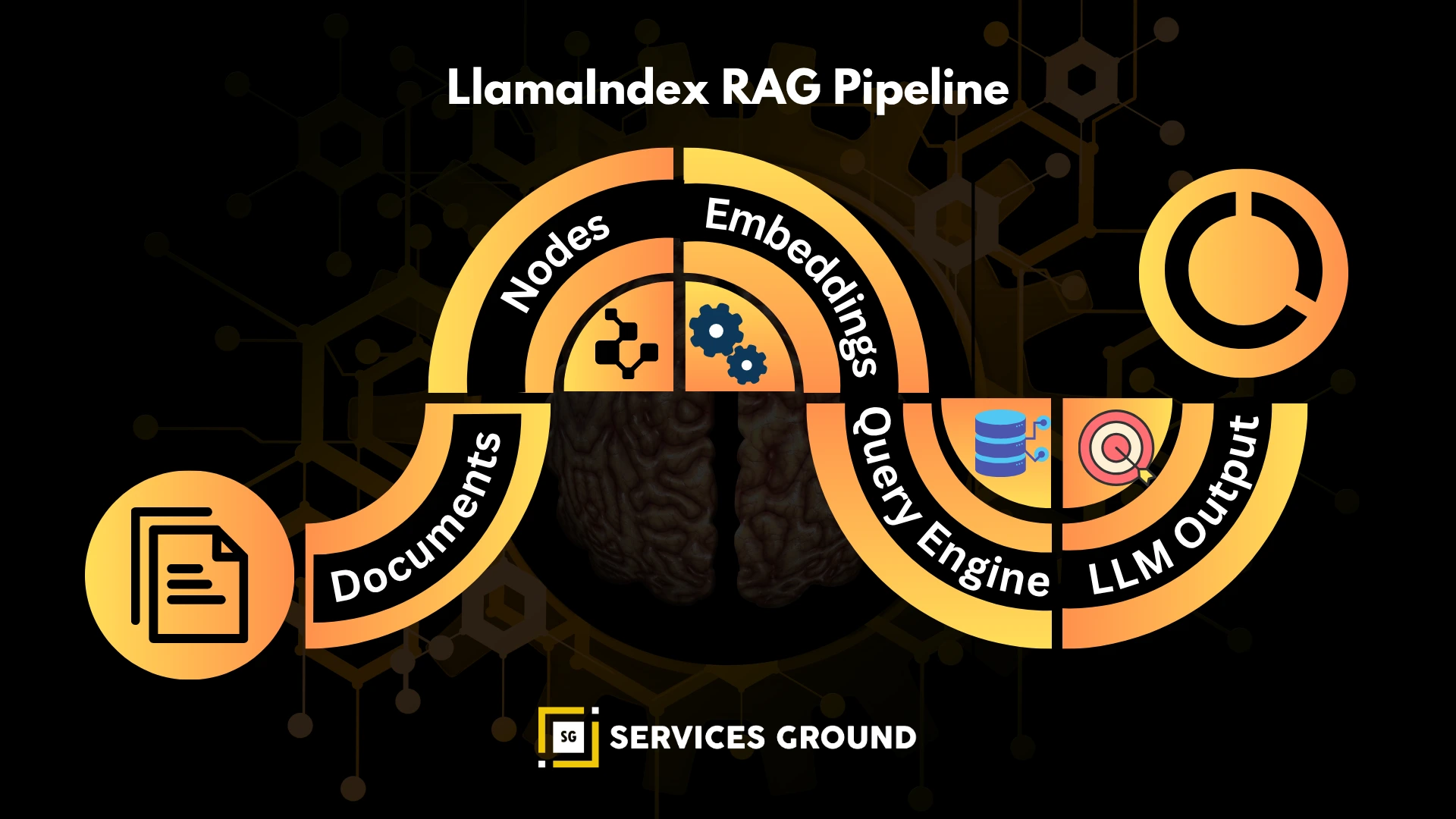
LlamaIndex — Data-Centric Orchestration & RAG Pipelines
LlamaIndex is the most advanced orchestration framework for:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Query pipelines
- Document-structured workflows
- Knowledge graphs
Key Capabilities
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| RAG-first architecture | Best for data-heavy workflows |
| Query engine | Structured retrieval pipelines |
| Tool & agent integration | Supports LLM logic |
| Document graphs | Build knowledge networks |
LlamaIndex Example
from llama_index.agent import ReActAgent from llama_index import SimpleDirectoryReader, VectorStoreIndex docs = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data() index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(docs) agent = ReActAgent.from_tools([index.as_query_engine()]) response = agent.chat("Compare AI orchestration frameworks.") print(response)
Strengths & Weaknesses
Strengths
- Market leader for RAG
- Best data indexing tools
- Clean pipeline design
Weaknesses
- Not meant for large multi-agent systems
Limited workflow controls
Comparison Table — LangGraph vs Semantic Kernel vs CrewAI vs LlamaIndex
| Feature | LangGraph | Semantic Kernel | CrewAI | LlamaIndex |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workflow Type | Graph / DAG | Skill planner | Role-based agents | RAG pipelines |
| Multi-Agent | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Enterprise Fit | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Observability | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| Best Use Case | Complex workflows | Enterprise copilots | Multi-agent teams | Knowledge workflows |
Real Use Cases for Orchestration Frameworks
1. Research & Writing Agents
- CrewAI = multi-agent team
- LlamaIndex = source retrieval
- LangGraph = step coordination
2. Customer Support Agents
- LangGraph = flows
- LlamaIndex = knowledge
- SK = governance
3. Code Generation / Review Pipeline
- CrewAI = roles (coder, reviewer, tester)
- LangGraph = workflow logic
4. Business Automation / Enterprise Ops
- SK = policy, security, logs
- LangGraph = reliable sequences
Which Framework Should You Choose? (Decision Guide)
Choose LangGraph if…
You need complex agent workflows, tool sequencing, or multi-step logic.
Choose Semantic Kernel if…
You’re building enterprise-grade copilots with compliance requirements.
Choose CrewAI if…
You need quick multi-agent pipelines with human-like collaboration.
Choose LlamaIndex if…
Your system is data-heavy, RAG-driven, or retrieval-centric.
Conclusion — The Infrastructure Layer of Agentic AI
AI orchestration frameworks are becoming the “operating system” of agentic AI.
They enable LLMs to:
- Act in multi-step flows
- Use tools safely
- Manage memory
- Collaborate with other agents
- Integrate with enterprise systems
- Execute long-running tasks
- Deliver deterministic, repeatable results
Choosing the right framework determines how far your agentic system can scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
AI orchestration frameworks coordinate LLM reasoning, tool usage, memory, workflows, and multi-agent collaboration to create structured, reliable AI systems.
LangGraph for complex workflows,
Semantic Kernel for enterprise copilots,
CrewAI for multi-agent teams,
LlamaIndex for RAG and data workflows.
Automating a multi-step customer support pipeline where the agent retrieves data, analyzes the request, takes action, and logs the interaction.
A system where multiple LLM agents—each with a role—collaborate, delegate tasks, and exchange information.
LangGraph, CrewAI, Semantic Kernel, LlamaIndex, and AutoGen (runner-up).
RAG manages data retrieval;
Orchestration manages workflow logic, agent actions, and tool calls.