Modern AI systems are impressive reasoners — but without reliable access to external knowledge, they hallucinate, forget, or generate outdated information.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) solves this by giving models access to real data during inference.
It is now the foundation for:
- Enterprise knowledge assistants
- Coding copilots
- Research and analysis agents
- Customer support bots
- Documentation Q&A
- Multi-step agentic workflows
As AI becomes more capable and agentic, RAG itself evolves—moving toward Agentic RAG, where retrieval is iterative, reasoning-driven, and stateful.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
RAG combines retrieval (searching for relevant knowledge) with generation (LLM reasoning) to produce grounded, up-to-date answers.
Why RAG exists:
| Problem | How RAG Fixes It |
|---|---|
| LLMs hallucinate | Provide factual context |
| Models have limited memory | Retrieve external docs on demand |
| Training data becomes outdated | Fetch latest information |
| No enterprise knowledge | Connect to private systems |
In short:
RAG = LLM + Search + Real Knowledge
How RAG Works
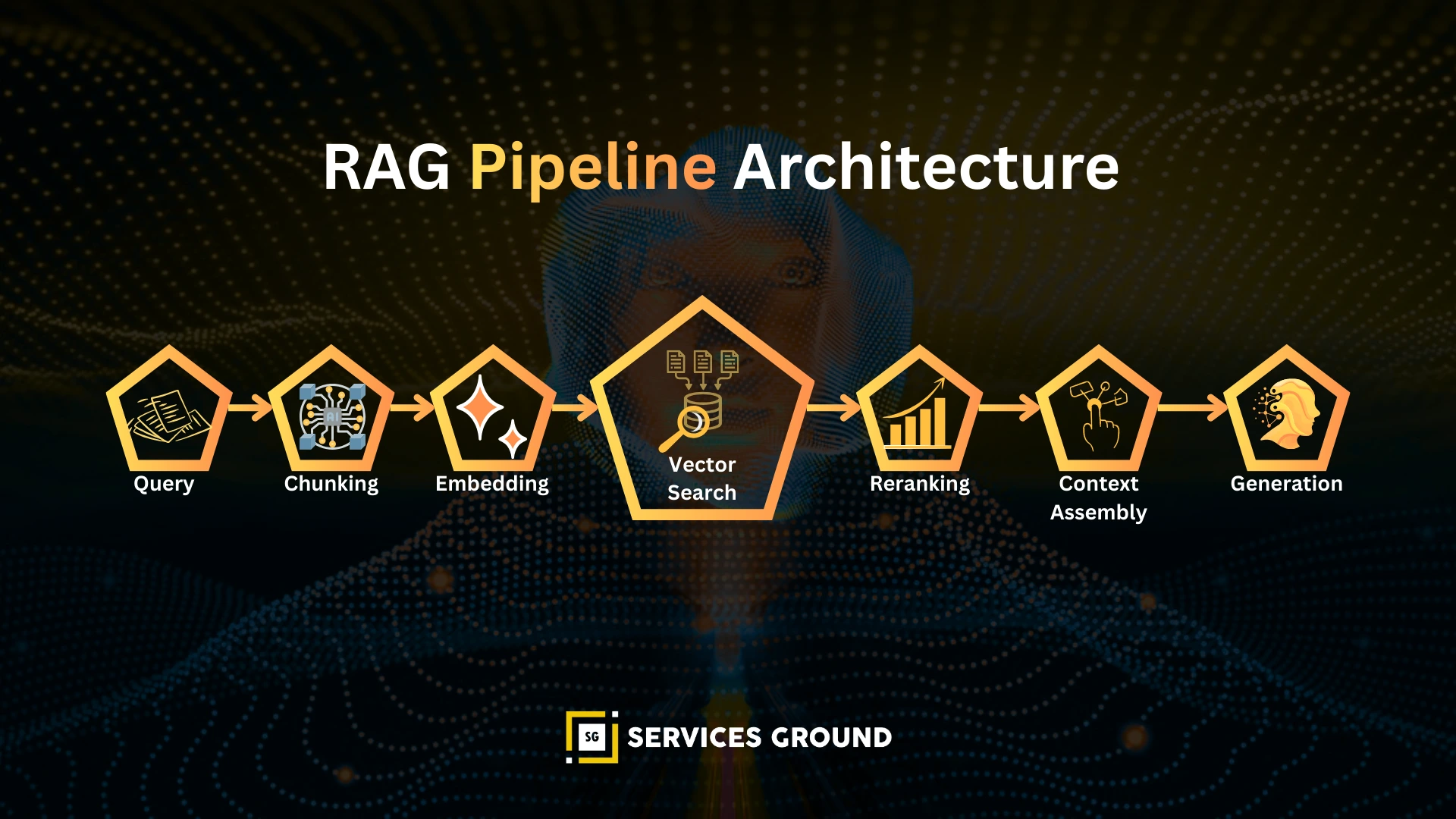
RAG has a 7-step flow:
- User Query → Understanding
- Chunking → Split documents
- Embedding → Vectorize chunks
- Vector Search → Retrieve top-k
- Reranking (optional)
- Compose Context → Inject into LLM
- Generation → Produce final answer
Each component dramatically affects quality.
For example, chunking alone affects up to 40% of retrieval accuracy.
Python RAG with OpenAI Embeddings + Vector Search
from openai import OpenAI import faiss import numpy as np client = OpenAI() # Indexing documents = ["RAG improves factual accuracy.", "Vector search retrieves relevant knowledge."] embeddings = client.embeddings.create( model="text-embedding-3-large", input=documents ).data vectors = np.array([e.embedding for e in embeddings]).astype("float32") index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(vectors.shape[1]) index.add(vectors) # Retrieval query = "How does RAG reduce hallucinations?" q_emb = client.embeddings.create( model="text-embedding-3-large", input=query ).data[0].embedding _, ids = index.search(np.array([q_emb]).astype("float32"), k=2) retrieved = [documents[i] for i in ids[0]] # Generation response = client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-4o-mini", messages=[ {"role": "system", "content": "Use retrieved context to answer."}, {"role": "assistant", "content": f"Context: {retrieved}"}, {"role": "user", "content": query} ] ) print(response.choices[0].message["content"])
Chunking Strategies
Most RAG failures are due to bad chunking.
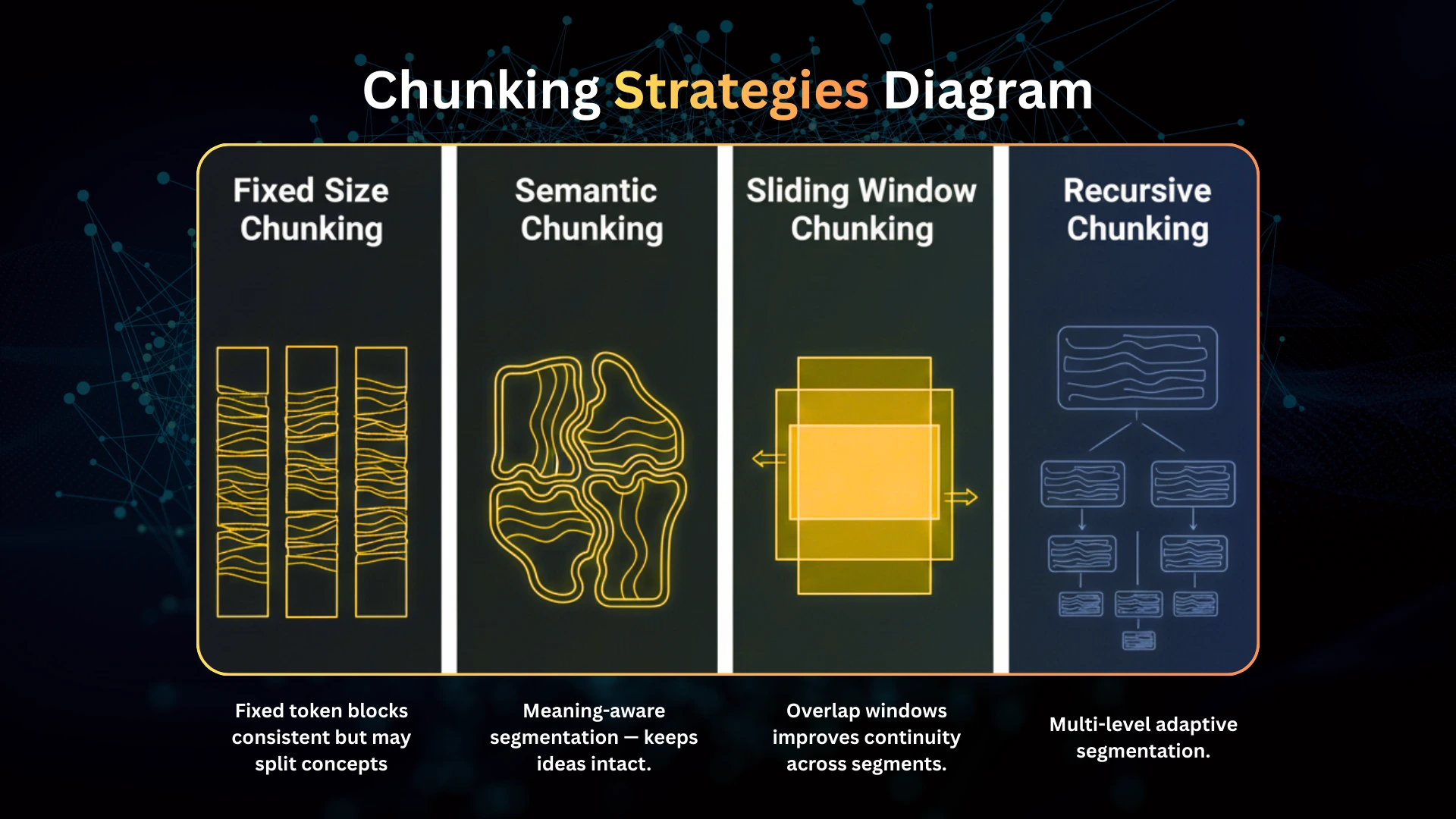
Common Chunking Methods
1. Fixed-Size Chunking
Simple, but often splits sentences mid-thought.
2. Recursive Semantic Chunking (LangChain)
Keeps semantic boundaries intact.
3. Sliding Window Chunking
Overlapping 50–100 tokens improves continuity.
4. Sentence Windowing
Highly effective for Q&A.
5. Document-Level Adaptive Chunking
Dynamic chunk-size based on structure.
Embeddings — Which Model Should You Use?
Different embeddings excel at different tasks.
| Model | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI text-embedding-3-large | General RAG | Fast, accurate, reliable | Paid |
| BGE Large | Open-source RAG | High recall | Heavy |
| Cohere Embed v3 | Enterprise search | Very high precision | Paid |
| E5 Large | Academic search | Good for QA | Slower |
| Voyage-large-2 | Chatbot retrieval | Best semantic match | Expensive |
Pro tip:
For 90% of use cases → OpenAI + reranking.
Vector Databases — Which One Should You Choose?
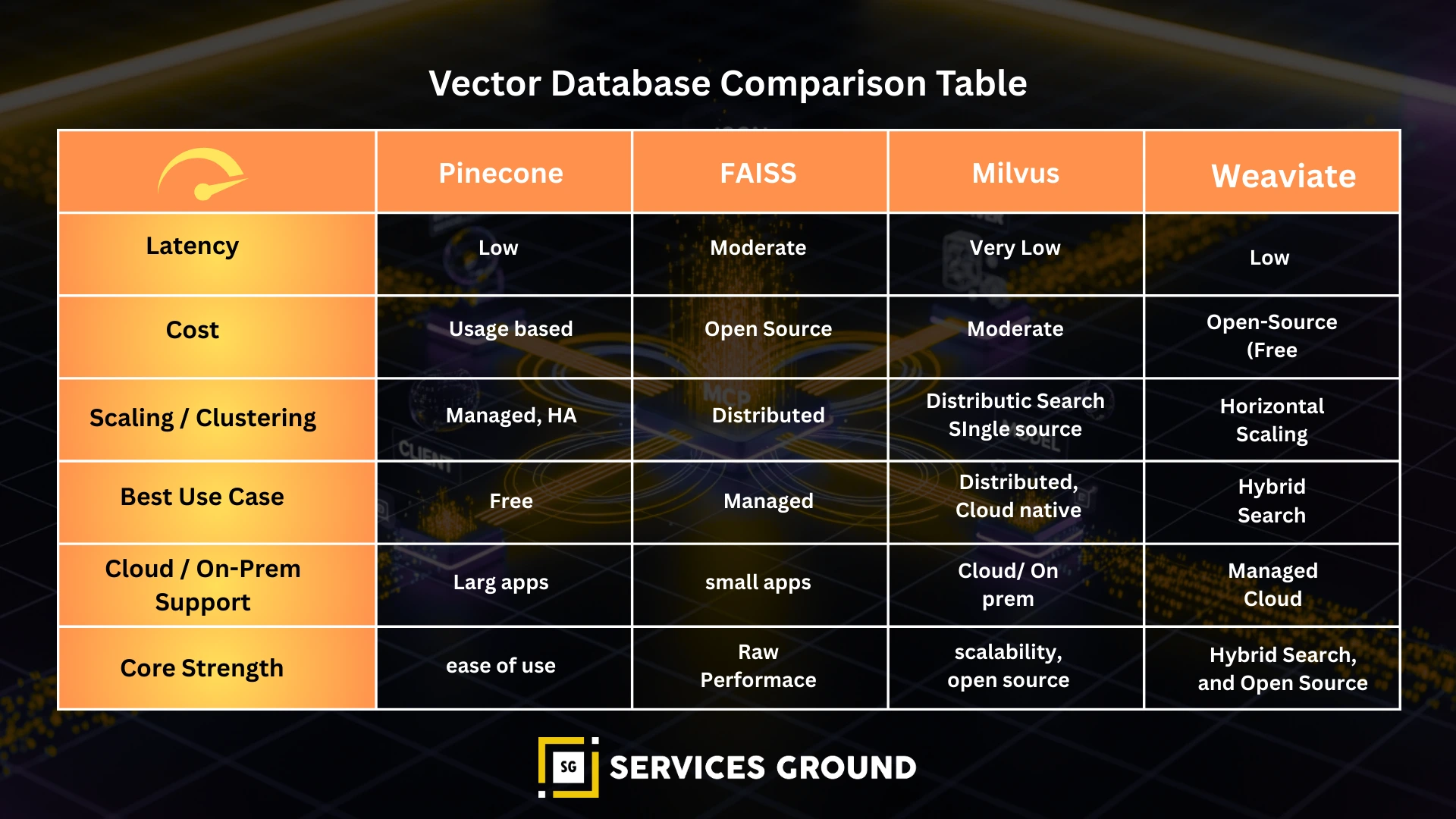
Comparison Table
| Database | Best For | Latency | Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinecone | Enterprise RAG | Low | High | Scalable & simple |
| Weaviate | Hybrid search | Medium | Medium | Built-in rerankers |
| Milvus | Large datasets | Very low | Low | Open-source |
| FAISS | Local testing | Very low | Free | Not managed |
Hybrid Retrieval (Sparse + Dense = Best Recall)
Dense retrieval (embeddings) ≠ enough.
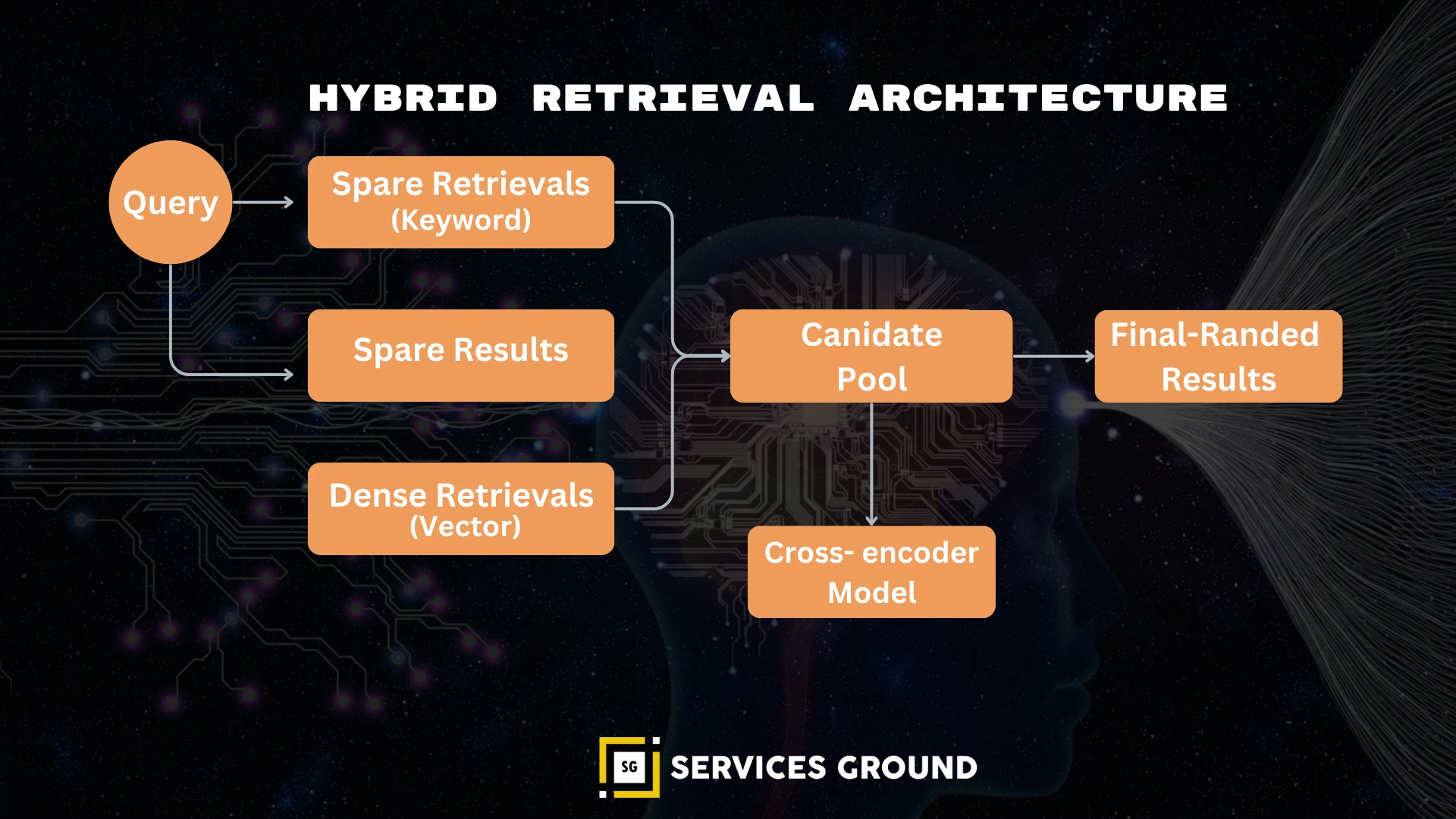
Combine with:
- BM25 → keyword precision
- Dense vectors → semantic recall
- Cross-encoder reranker → relevance re-scoring
This gives the highest accuracy in production RAG systems.
Advanced RAG Techniques
Multi-Hop Retrieval (Agentic RAG)
The model retrieves → reasons → retrieves deeper.
Example:
- Retrieve high-level docs
- Extract sub-topics
- Retrieve deeper information
- Repeat until answer is complete
This is used in research agents and data-intensive copilots.
GraphRAG
Key idea:
Structured knowledge > bag-of-chunks.
GraphRAG uses:
- Knowledge graphs
- Entities
- Relationships
- Subgraphs
- Path reasoning
Great for enterprise knowledge bases.
Reranking with Cross-Encoders
Dense vectors = retrieve 20
Cross-encoder = rank top 5
LLM = answer with top 5
Highest accuracy pipeline.
LlamaIndex Advanced RAG Example
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding docs = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data() index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents( docs, embed_model=OpenAIEmbedding(model="text-embedding-3-large") ) query_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5) response = query_engine.query("Explain RAG.") print(response)
LangChain RAG Example (with Reranking)
from langchain.retrievers import BM25Retriever, EnsembleRetriever from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings dense = OpenAIEmbeddings() bm25 = BM25Retriever.from_texts(docs) ensemble = EnsembleRetriever(retrievers=[dense, bm25], weight=[0.7, 0.3]) result = ensemble.get_relevant_documents("what is hybrid retrieval?") print(result)
RAG Evaluation — Measuring Real Quality
Evaluation signals:
- Retrieval recall
- Context relevance
- Faithfulness (is answer grounded?)
- Factual accuracy
- Hallucination rate
- Embedding drift
- Index freshness
Tools:
- Ragas
- DeepEval
- TruLens
LlamaIndex Evaluation
RAG Failure Modes (And How to Fix Them)
| Failure | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Irrelevant retrieval | Bad embeddings | Use reranking |
| Hallucinations | Missing context | Hybrid retrieval |
| Wrong documents | Bad chunking | Semantic splitting |
| Too long context | Context flooding | Rerank + filter |
| Inconsistent answers | Missing metadata | Add document IDs |
| Slow performance | Large vectors | ANN indexes |
Real-World Use Cases
- Coding copilots
- AI customer support
- Enterprise knowledge search
- Research assistants
- Documentation Q&A
- Legal & medical retrieval
- Product search
News analysis bots
Conclusion — The Future of RAG is Agentic
RAG is no longer just about retrieving documents — it’s evolving into iterative, reasoning-driven retrieval that powers multi-agent and autonomous AI systems.
By combining:
- Better chunking
- Stronger embeddings
- Hybrid retrieval
- Multi-hop reasoning
- Graph-based retrieval
- Structured memory
- Orchestration frameworks
Developers can build AI systems that are not only factual, but contextually intelligent, explainable, and trustworthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is a technique that enhances LLM responses by retrieving relevant external documents.
A chatbot that reads private company documents and answers questions based on them.
By grounding answers in retrieved facts rather than relying solely on model memory.
A retrieval method combining dense vectors + keyword-based search + reranking.
Pinecone for enterprise, Weaviate for hybrid search, FAISS for local testing.