Agentic AI Safety, Security, and Governance
Agentic AI safety, security, and governance focus on controlling autonomous system behavior, tool execution, data access, and decision boundaries to prevent harm. Unlike traditional AI systems, agentic AI systems act in real environments, use tools, and retain memory, which increases operational and organizational risk.
As autonomy increases, controlling outcomes becomes harder. Safety frameworks, security boundaries, and governance models exist to keep agent behavior aligned with human intent and legal responsibility.
What is agentic AI safety, security, and governance?
Agentic AI safety ensures autonomous agents behave within defined goals and constraints.
Agentic AI security enforces technical boundaries around tools, data, and execution environments.
Agentic AI governance assigns ownership, accountability, and oversight for agent behavior.
These layers apply to systems that can:
- Execute actions
- Call tools or APIs
- Persist memory across tasks
- Interact with browsers, files, or users
Traditional AI focuses on output quality. Agentic AI requires behavioral control.
Understanding risk sources comes next.
What risks do agentic AI systems introduce?
Agentic AI systems introduce risks through autonomy, execution capability, memory persistence, and environment interaction. These risks originate from how agents operate, not only from model accuracy.

Risk categories by mechanism
| Risk category | Mechanism | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy risk | Unbounded goal pursuit | Agent repeats a harmful task |
| Tool misuse risk | Excessive permissions | Shell tool deletes files |
| Data exposure risk | Persistent memory | PII stored in vector memory |
| Environment risk | Browser or OS control | Unauthorized web actions |
| Coordination risk | Multi-agent interaction | Conflicting agent decisions |
Classifying risks by mechanism makes mitigation and governance measurable.
This also explains why agent security differs from traditional AI security.
Why does agentic AI security differ from traditional AI security?
Agentic AI security differs because agents perform actions, not just generate text.
Traditional AI security focuses on:
- Prompt manipulation
- Output filtering
- Model misuse
Agentic AI security must also manage:
- Tool invocation
- Permission scope
- Execution environments
- State persistence
Once systems can act, security shifts from content control to execution control.
Governance defines who is responsible for that control.
What does governance mean in agentic AI systems?
Governance in agentic AI defines who sets constraints, who monitors behavior, and who intervenes when agents fail. It operates at the organizational level rather than the model level.
Governance responsibilities include:
- Defining acceptable agent behavior
- Approving tool access
- Reviewing logs and decisions
- Managing incidents and failures
Without governance, safety lacks authority and security lacks accountability.
Controls make governance enforceable.
Which safety control categories exist for agentic AI?
Agentic AI safety relies on layered control categories, not single safeguards.
Core control categories
- Preventive controls
Restrict actions before execution.
- Detective controls
Observe, trace, and record behavior.
- Corrective controls
Stop, roll back, or recover after failure.
- Governance controls
Define approval, responsibility, and review.
Each category addresses a different failure mode. Combined controls reduce systemic risk.
These layers operate together.
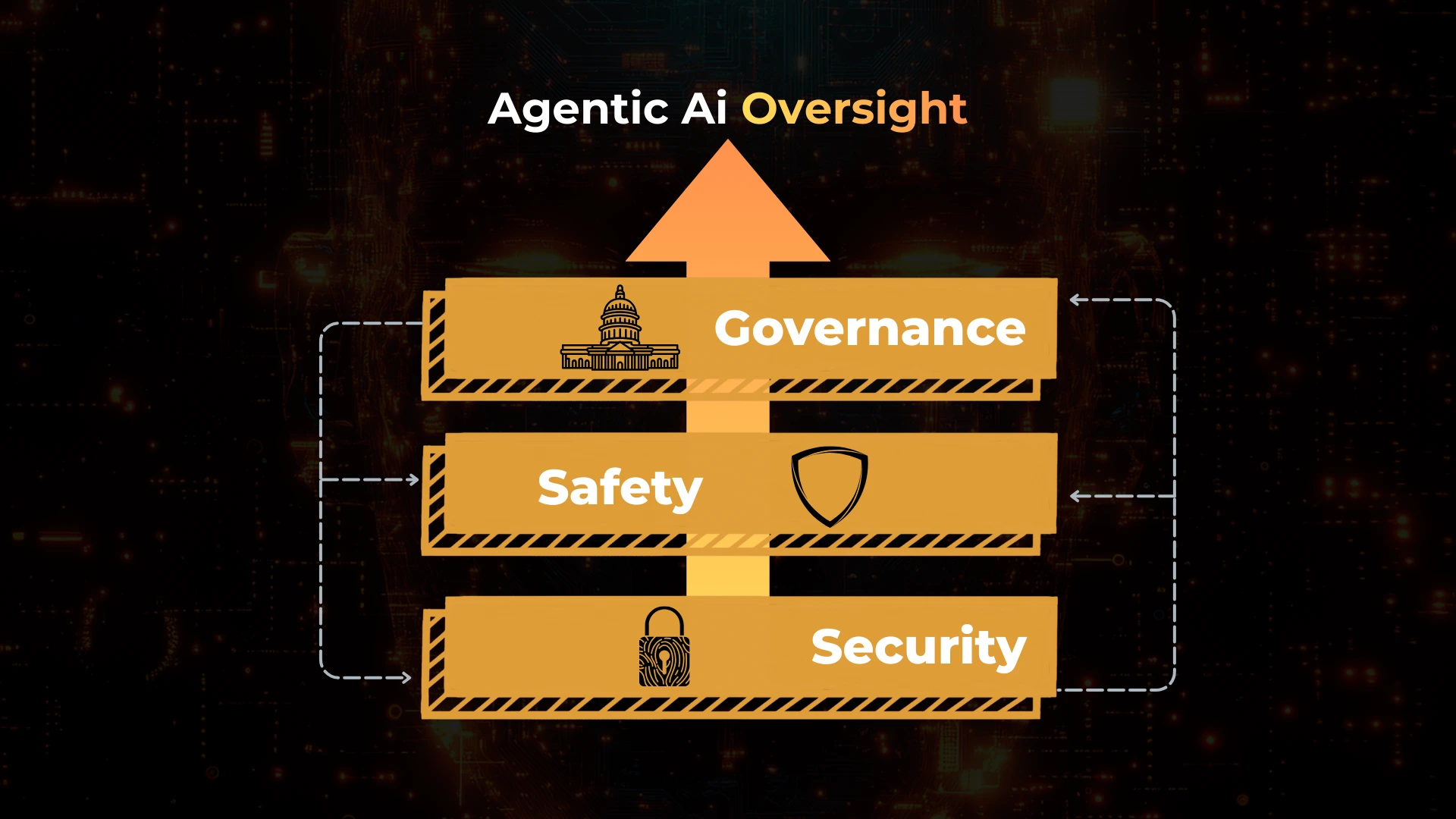
How do safety, security, and governance interact?
Safety defines acceptable outcomes.
Security enforces technical boundaries.
Governance ensures accountability and oversight.
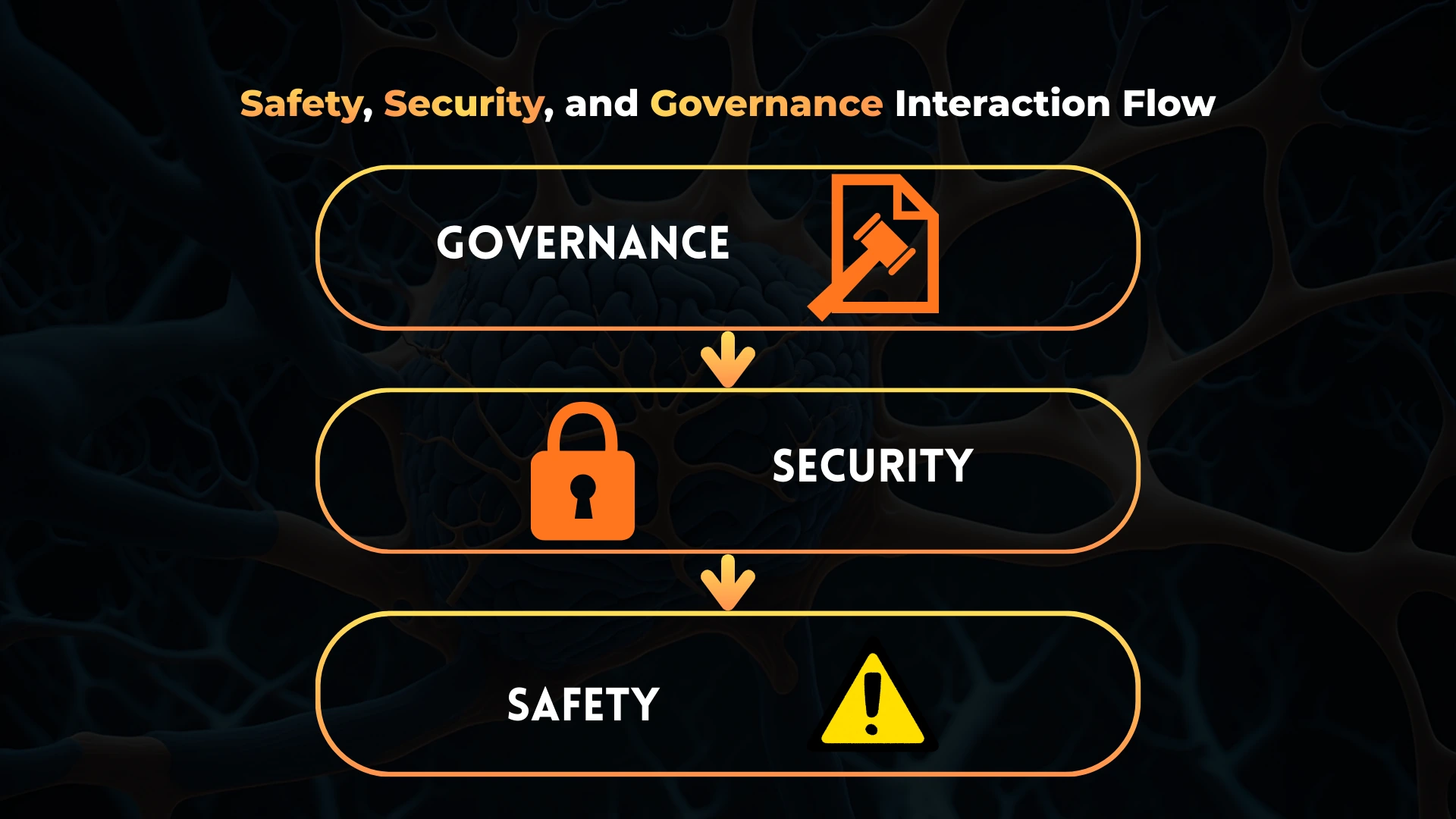
The interaction follows a clear flow:
- Governance defines policies and responsibility
- Security enforces permissions and execution limits
- Safety evaluates outcomes and behavior
Weakness in any layer destabilizes the system.
Certain conditions increase governance requirements.
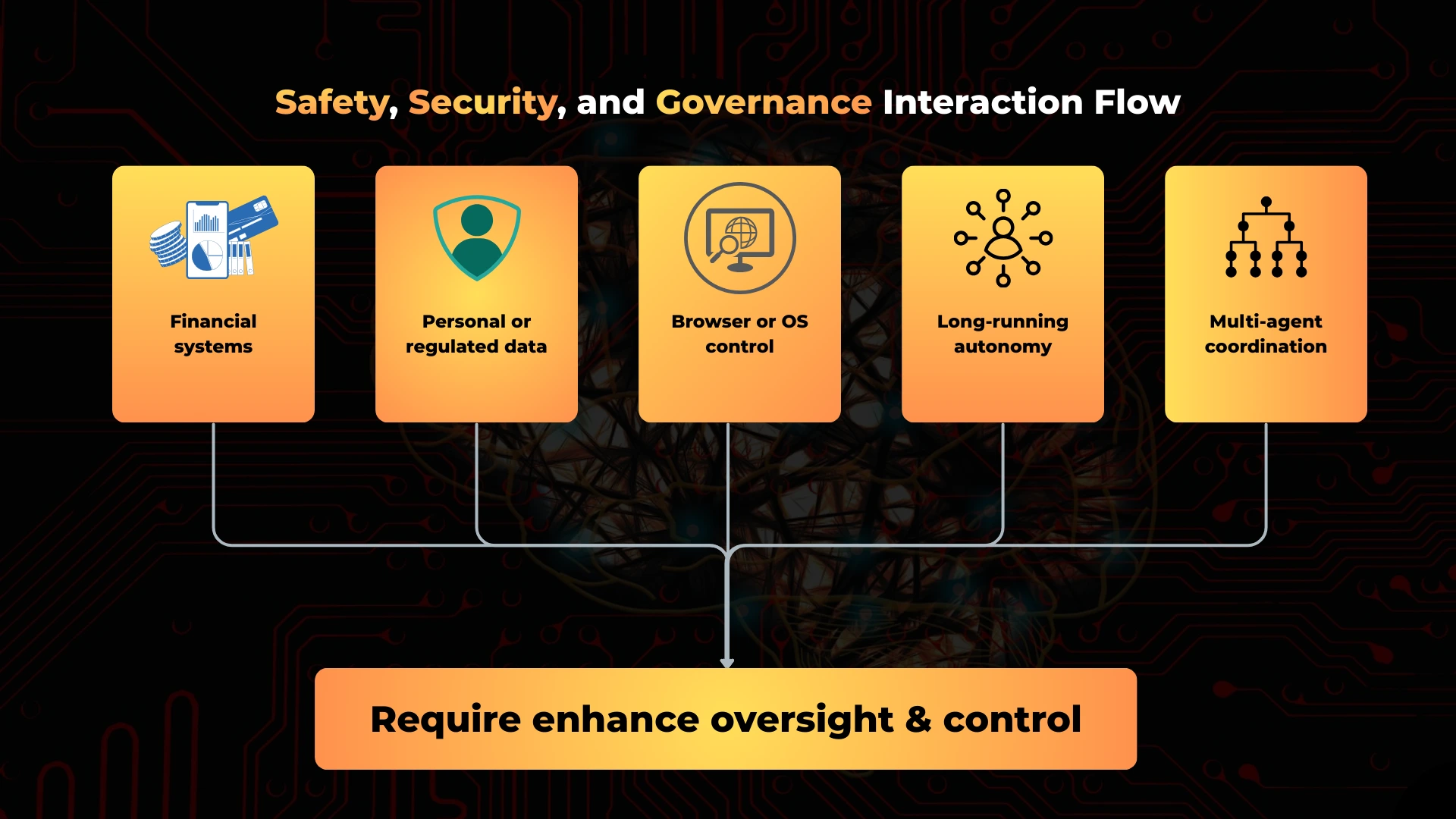
When do agentic AI systems require stricter governance?
Stricter governance becomes necessary when agents operate in high-impact environments.
Common triggers include:
- Access to financial systems
- Handling regulated or personal data
- Browser or operating system control
- Long-running autonomous execution
- Multi-agent coordination
As impact grows, informal oversight fails. Formal governance becomes mandatory.
Evaluation confirms whether controls work.
How is agentic AI safety evaluated at a high level?
Agentic AI safety is evaluated through behavioral assessment rather than output accuracy alone.
High-level evaluation focuses on:
- Action success and failure rates
- Permission boundary violations
- Logging completeness
- Recovery effectiveness
These checks confirm whether safety, security, and governance function together as intended.
Operational guidance builds on these principles.
What comes next after understanding agentic AI safety?
Safety principles only become effective when applied through concrete controls. The next step is exploring how risks are mitigated in practice through permission models, audit logging, sandboxing, and incident response.
Those operational mechanisms translate governance decisions into enforceable system behavior.
Conclusion
Agentic AI systems introduce new risks because they act, persist state, and interact with real environments. Safety defines acceptable behavior, security enforces boundaries, and governance assigns responsibility. Together, these layers make autonomous systems controllable, auditable, and accountable as autonomy increases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Agentic AI safety focuses on controlling autonomous agent behavior, actions, and decision boundaries to prevent harm during real-world execution.
Agentic AI security controls tool execution, permissions, and environments, while LLM security mainly addresses prompt abuse and output filtering.
Governance assigns ownership, approval, and accountability for agent behavior, ensuring safety and security controls are enforceable.
Key risks include unbounded autonomy, tool misuse, data leakage through memory, environment control abuse, and multi-agent coordination failures.
Stricter governance is required when agents access sensitive data, financial systems, browsers, operating systems, or operate autonomously for long durations.