Evaluation & Benchmarks for Agentic AI Systems
As AI systems evolve from single-prompt models into autonomous, multi-step agents, the question is no longer how smart is the model, but how reliably can the system act. Agentic AI introduces planning, memory, tool use, environment interaction, and long-horizon decision-making. These capabilities fundamentally change how AI must be evaluated.
Traditional benchmarks designed for static language models fail to capture the behaviors that define agentic systems. Measuring accuracy on fixed datasets is insufficient when an agent must reason, adapt, recover from failure, coordinate tools, and operate in dynamic environments.
What Does “Evaluation” Mean for Agentic AI?
Evaluation in agentic AI measures system behavior, not just model output.
Unlike standard LLM evaluation, agent evaluation must account for:
- Multi-step reasoning and planning
- Tool and API interaction
- State persistence and memory usage
- Environmental awareness
- Error recovery and retries
- Long-term goal completion
- Autonomy under uncertainty
An agent is not evaluated on a single response, but on its trajectory of actions over time.
Agent evaluation answers questions such as:
- Did the agent choose the right tools?
- Did it plan effectively?
- Did it recover from errors?
- Did it complete the task within constraints?
- Did it behave safely and predictably?
This shifts evaluation from output correctness to behavioral reliability.
Why Traditional Benchmarks Fail for Agentic Systems
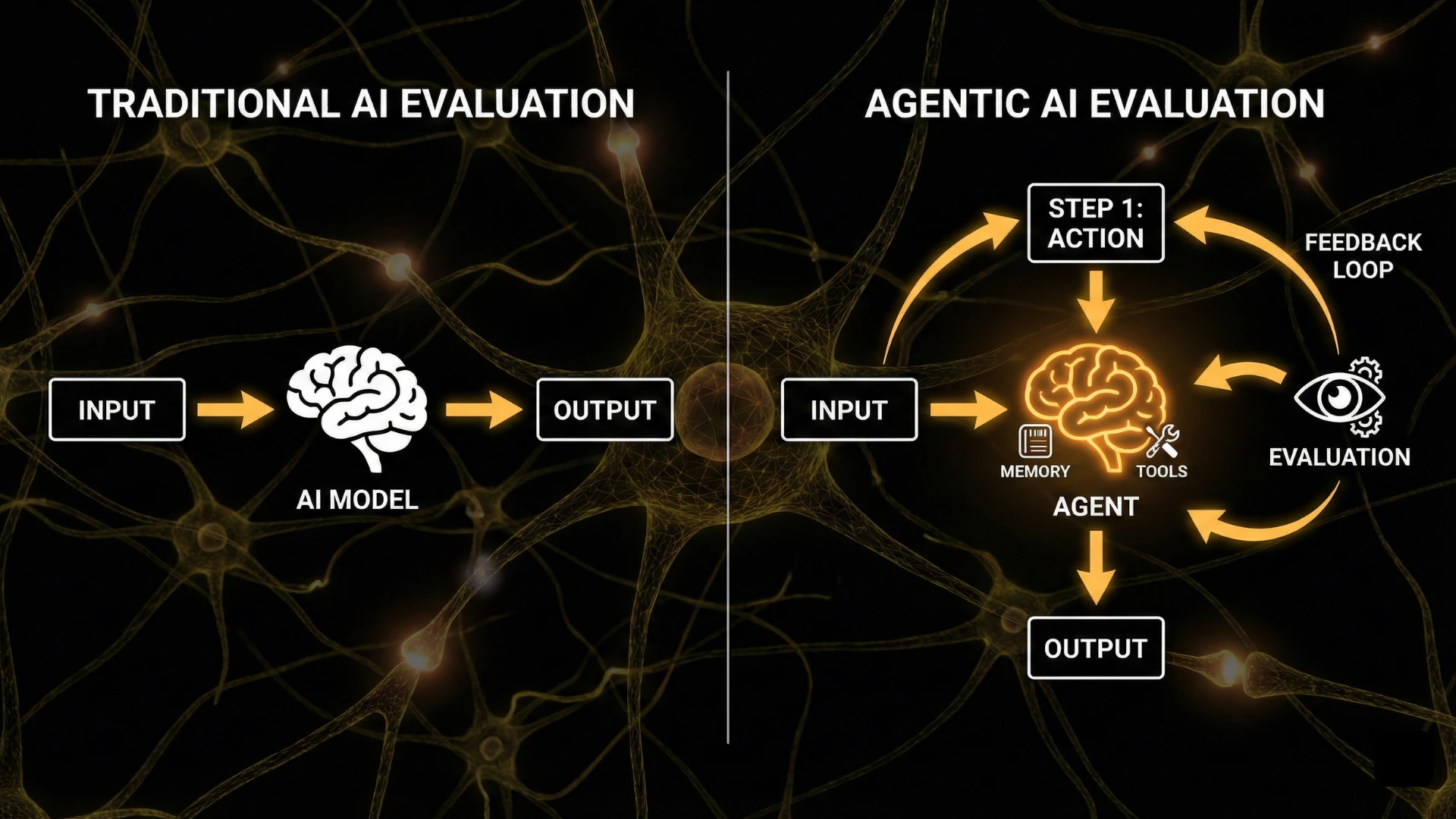
Classic AI benchmarks assume a static interaction model:
- One input
- One output
- One correctness score
Agentic systems violate all three assumptions.
Static Benchmarks Ignore Action Sequences
Agents act in sequences. A correct final answer may hide poor reasoning, inefficient planning, or unsafe intermediate steps. Conversely, a temporary failure may still lead to successful task completion after recovery.
They Cannot Measure Tool Use
Traditional benchmarks do not evaluate whether an agent:
- Selected the right tool
- Passed correct parameters
- Interpreted tool responses accurately
- Avoided unnecessary or unsafe calls
They Ignore Environment Dynamics
Real agents operate in environments that change:
- Websites update
- APIs return partial failures
- Filesystems evolve
- State can drift over time
Static benchmarks cannot model these dynamics.
They Fail to Capture Long-Horizon Behavior
Many agent tasks span minutes, hours, or days. Short benchmarks miss:
- Memory degradation
- Planning collapse
- Error accumulation
- Feedback loops
As a result, classic benchmarks systematically overestimate real-world agent reliability.
Core Dimensions of Agentic AI Evaluation
Effective agent evaluation must be multi-dimensional. No single metric captures agent performance.
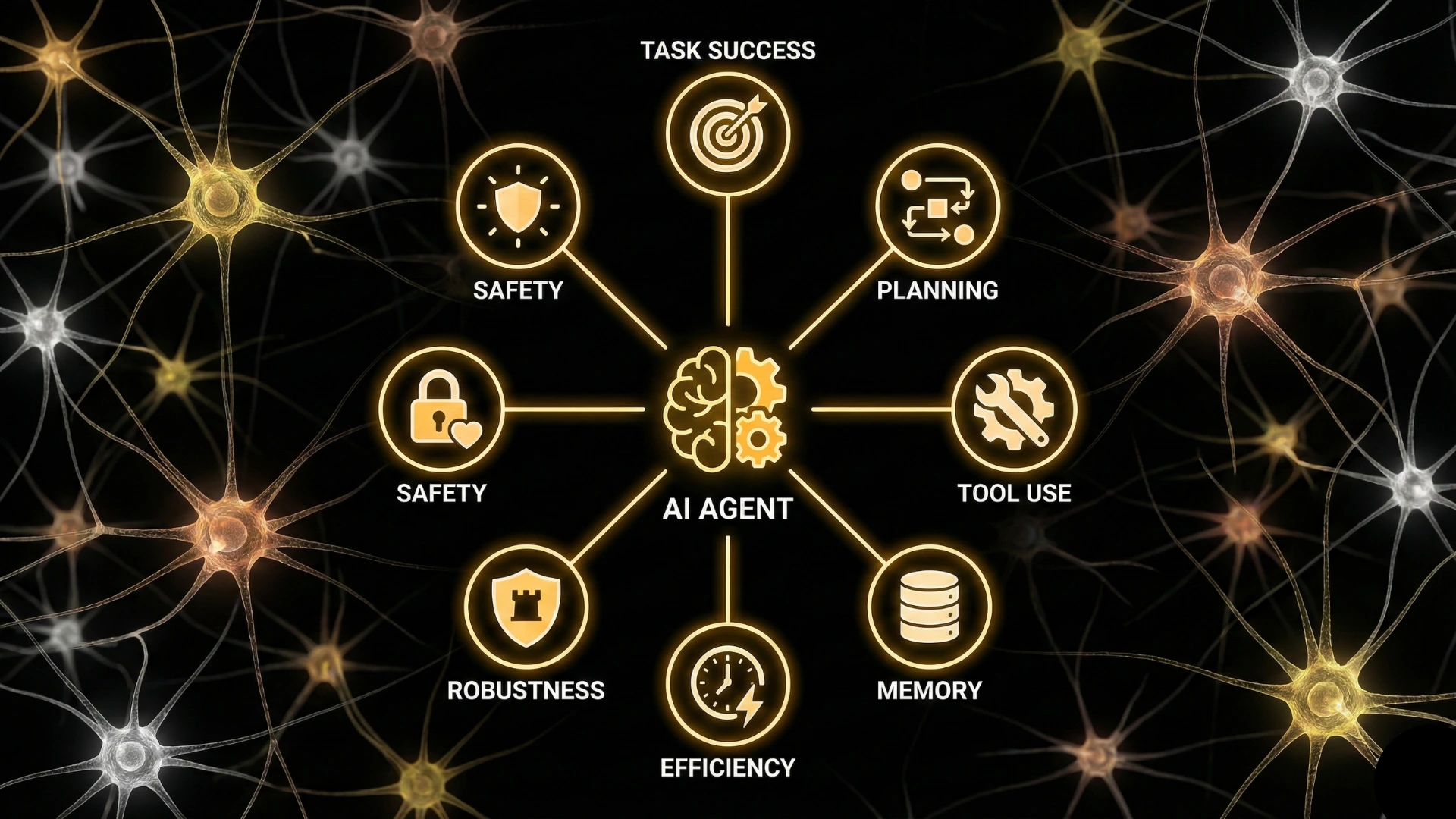
1. Task Success and Completion Rate
At the highest level, evaluation asks:
- Did the agent complete the task?
- Did it meet defined success criteria?
This is often binary, but must be contextualized by task difficulty and constraints.
2. Planning and Reasoning Quality
Agents must decompose goals into steps.
Evaluation includes:
- Plan coherence
- Step ordering
- Adaptation when plans fail
- Avoidance of unnecessary actions
Poor planning often leads to tool misuse, wasted computation, or unsafe behavior.
3. Tool Use and Action Correctness
For tool-enabled agents, benchmarks must assess:
- Tool selection accuracy
- Argument correctness
- Response interpretation
- Retry logic and fallback behavior
This dimension is central to real-world agent reliability.
4. Memory and State Management
Agent memory must be evaluated across:
- Short-term context
- Long-term knowledge
- Episodic memory (past actions and outcomes)
Key questions include:
- Does the agent recall relevant information?
- Does memory drift or degrade?
- Does stale memory cause errors?
5. Efficiency and Resource Use
Agents consume:
- Tokens
- API calls
- Time
- Compute resources
Evaluation must consider:
- Cost per task
- Latency
- Redundant actions
- Scalability under load
6. Robustness and Error Recovery
Real environments fail. Evaluation must measure:
- How often agents encounter errors
- Whether they recover gracefully
- Whether failures cascade or terminate workflows
7. Safety, Control, and Predictability
Agent evaluation must include:
- Constraint adherence
- Avoidance of unsafe actions
- Predictable behavior under edge cases
- Alignment with human intent
Types of Benchmarks for Agentic AI
Agentic evaluation benchmarks are emerging across several categories, each targeting a different capability.
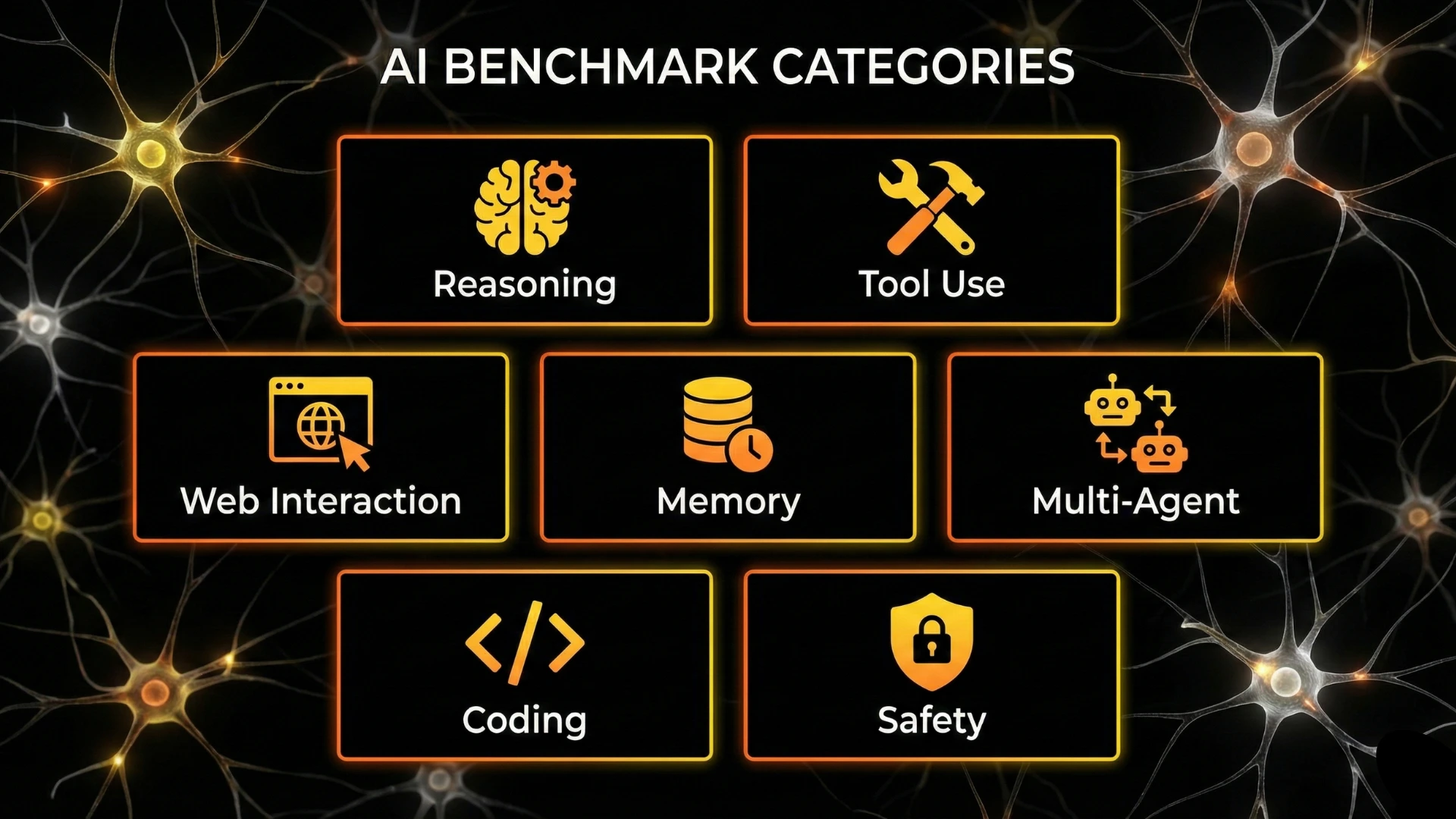
Reasoning and Planning Benchmarks
These benchmarks test an agent’s ability to:
- Decompose goals
- Maintain logical consistency
- Adapt plans when information changes
They often involve:
- Multi-step puzzles
- Task decomposition challenges
- Sequential decision problems
Tool Use and Function Calling Benchmarks
These benchmarks evaluate:
- API usage
- Tool orchestration
- Parameter accuracy
- Error handling
They are essential for production agents that interact with software systems.
Web and Computer Interaction Benchmarks
These focus on agents operating graphical or web environments:
- Browsing websites
- Filling forms
- Navigating UIs
- Interacting with dynamic DOMs
They test perception, grounding, and action reliability.
Memory and Retrieval Evaluation
These benchmarks assess:
- Retrieval accuracy
- Context relevance
- Long-term recall
- Memory update strategies
They are closely tied to RAG and agent memory architectures.
Multi-Agent Coordination Benchmarks
These evaluate:
- Task decomposition across agents
- Communication efficiency
- Conflict resolution
- Role specialization
They reflect real-world distributed agent systems.
Coding and Software Engineering Agent Benchmarks
These test:
- Code generation
- Debugging
- Repository navigation
- Test execution
- Iterative refinement
They are increasingly important in developer-facing agent applications.
Safety and Reliability Benchmarks
These measure:
- Constraint violations
- Unsafe actions
- Hallucinated tool calls
- Misalignment under stress conditions
Safety evaluation is mandatory for real deployment.
Evaluation Methodologies: How Agents Are Actually Measured
Agent evaluation is not just about datasets; it is about experimental design.
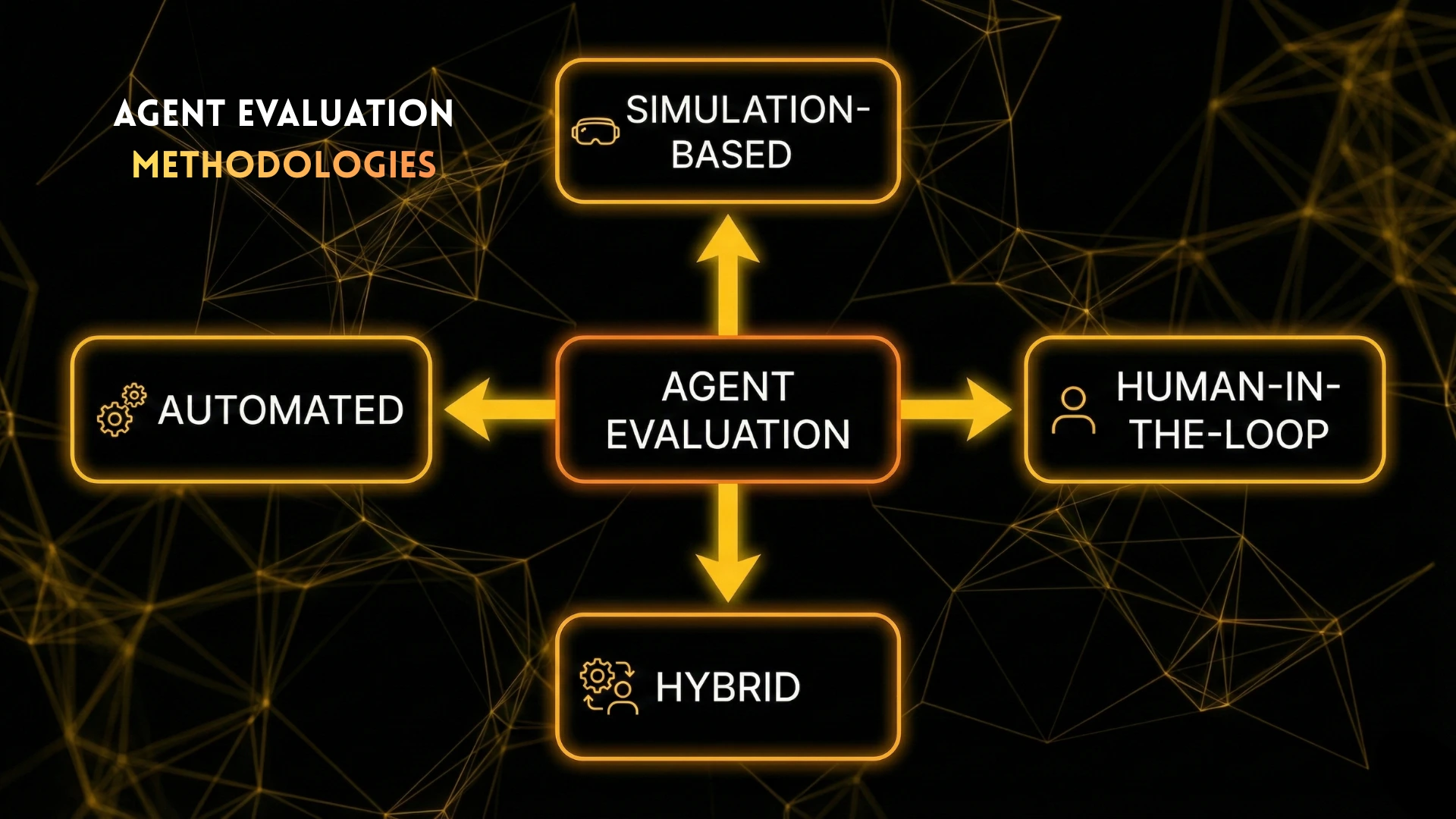
Automated Evaluation
Automated methods include:
- Scripted success checks
- Environment state validation
- Log analysis
- Deterministic replay
They scale well but may miss subtle failures.
Simulation-Based Evaluation
Agents are tested in controlled environments that simulate:
- Web apps
- Operating systems
- APIs
- User behavior
This allows repeatability while preserving realism.
Human-in-the-Loop Evaluation
Human reviewers assess:
- Decision quality
- Safety
- Usefulness
- Explanation clarity
This is expensive but essential for nuanced judgment.
Hybrid Evaluation
Most serious systems use:
- Automated metrics for scale
- Human review for critical cases
Hybrid evaluation is the current best practice.
Why Agent Evaluation Is a Systems Problem
Agent performance is not determined by the model alone.
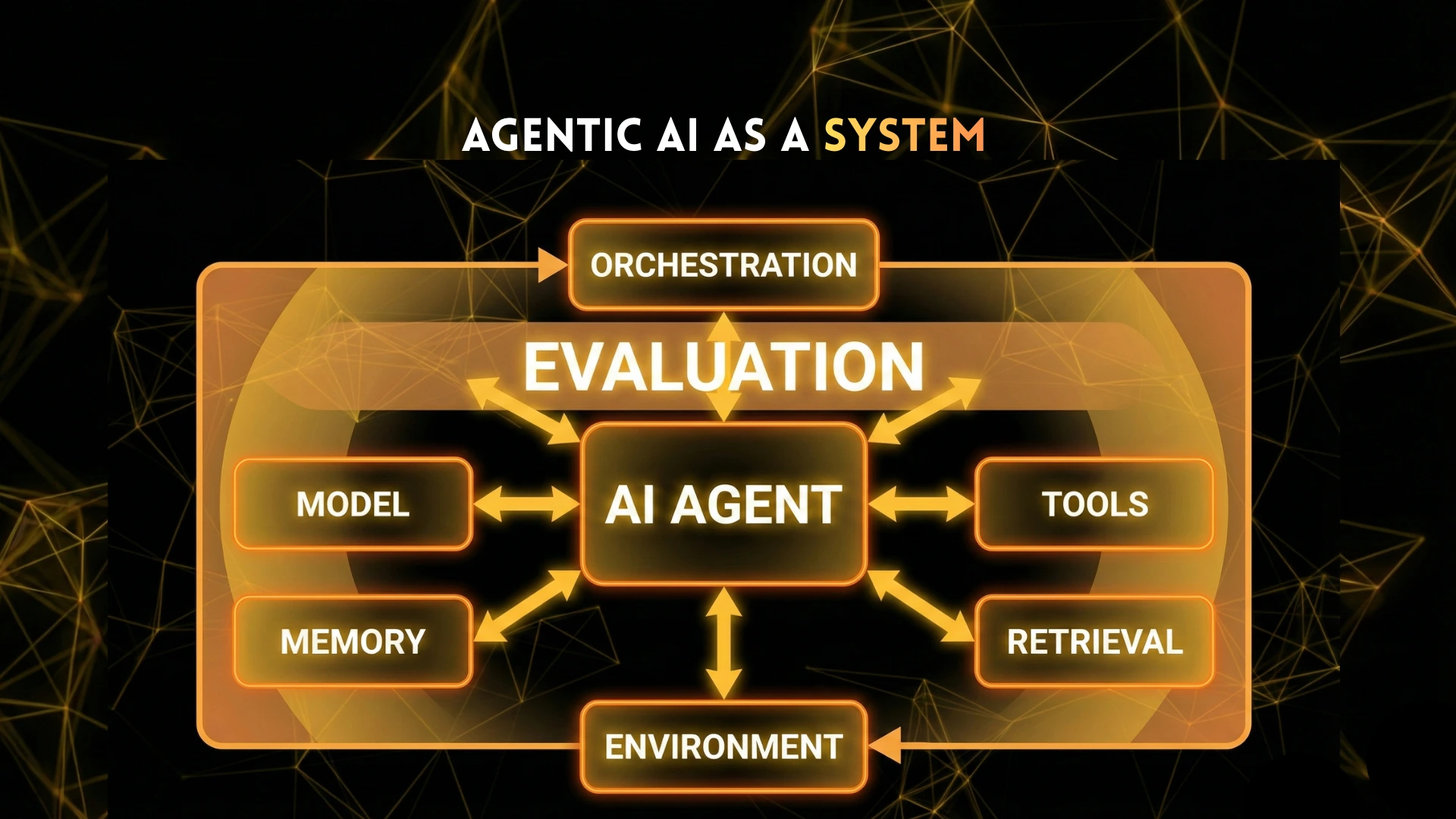
Evaluation must consider the entire stack:
- Model
- Prompting
- Memory
- Retrieval
- Tools
- Orchestration
- Environment
A strong model with weak orchestration can fail.
A modest model with strong systems design can outperform expectations.
Benchmarks that isolate the model miss these interactions entirely.
Common Evaluation Failures in Production
Organizations repeatedly encounter the same issues.
Over-Optimizing for Single Metrics
Agents optimized for one metric often fail elsewhere:
- Fast but unsafe
- Accurate but slow
- Cheap but unreliable
Balanced evaluation is essential.
Benchmark Overfitting
Agents trained to pass specific benchmarks often:
- Exploit quirks
- Fail in slightly different environments
- Collapse under real-world variability
Ignoring Long-Horizon Behavior
Short tests miss:
- Memory drift
- Planning collapse
- Accumulated errors
Long-running evaluation is required.
The Role of Benchmarks in Building Trustworthy Agents
Evaluation is not a marketing exercise. It is a control mechanism.
Robust benchmarks:
- Surface failure modes early
- Guide system design decisions
- Enable safe scaling
- Support governance and compliance
Without rigorous evaluation, agentic AI remains unreliable by design.
Conclusion
Agentic AI systems demand a fundamentally new approach to evaluation and benchmarking. Measuring isolated outputs is no longer sufficient when systems plan, act, adapt, and learn over time.
Effective agent evaluation:
- Focuses on behavior, not just answers
- Measures systems, not models
- Balances automation with human judgment
- Scales across complexity and time
As agentic AI becomes embedded in real workflows, evaluation is no longer optional. It is the foundation that determines whether agents are trustworthy, scalable, and safe to deploy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Agentic AI evaluation is the process of measuring how well an AI agent performs complex, multi-step tasks involving reasoning, tool use, memory, and interaction with dynamic environments. Unlike traditional model evaluation, it assesses behavior across entire workflows rather than single responses.
Traditional benchmarks focus on static inputs and outputs, such as question answering or classification accuracy. Agentic AI systems operate over time, make decisions, use tools, and adapt to changing contexts, which requires system-level evaluation rather than isolated task scoring.
Common agent evaluation metrics include task success rate, planning accuracy, tool usage correctness, memory consistency, latency, robustness to errors, safety behavior, and overall reliability across multiple steps.
Autonomous AI agents are benchmarked using task environments, simulations, and controlled workflows where agents must complete objectives using reasoning, tools, and memory. Performance is measured across success rates, efficiency, failure recovery, and consistency.
AI model evaluation measures the quality of model outputs in isolation, while AI agent evaluation measures end-to-end system behavior, including decision-making, action execution, state tracking, and interaction with external tools or environments.
Agentic AI benchmarks are standardized tasks or environments designed to test agent capabilities such as planning, web navigation, tool use, coding, memory retention, and multi-agent coordination. Examples include web-based task environments and tool-interaction benchmarks.
Browser-based AI agents are evaluated by measuring their ability to navigate websites, interact with user interfaces, extract information, and complete tasks reliably in realistic web environments while handling errors and dynamic page changes.
Human-in-the-loop evaluation involves human reviewers validating agent actions, decisions, and outcomes. It is often used to assess correctness, safety, and usability when automated metrics alone cannot capture qualitative behavior.
Long-term memory evaluation measures how well an agent stores, retrieves, updates, and uses past information across multiple tasks or sessions. This includes checking for memory consistency, relevance, and avoidance of outdated or conflicting information.
Multi-agent benchmarks evaluate coordination, communication, role specialization, and conflict resolution among multiple agents working toward shared or competing goals. These benchmarks focus on system-level collaboration rather than individual agent performance.
Latency is critical for agentic systems, especially those performing multi-step reasoning or real-time interaction. High latency can break workflows, reduce usability, and degrade overall agent performance even if task success rates are high.
Yes. Several open-source tools and research environments support agent evaluation, including simulation environments, web-interaction benchmarks, and orchestration frameworks that log agent behavior for structured analysis.
The biggest challenge is capturing real-world complexity. Agentic systems operate in open-ended environments with uncertainty, partial observability, and long-term dependencies, making standardized, repeatable evaluation difficult.
AI agents should be continuously evaluated, especially after changes to models, tools, memory systems, or workflows. Ongoing evaluation helps detect performance regressions, safety issues, and unexpected behavior.
Benchmarks provide useful signals but cannot fully predict real-world performance. Production environments often introduce variability, edge cases, and user behavior that exceed controlled benchmark conditions.
The future of agentic AI evaluation lies in system-level benchmarks, adaptive environments, continuous monitoring, and combined automated and human evaluation pipelines that better reflect real-world deployment conditions.