The search engine consists of three key components:
- Search Engine Goals
- Indexing
- Crawling
Too much of your business depends on being noticeable in your search engines. You’d like to try to grasp this thing that has so much control over your career.
But finding out how search engines operate can be very challenging. And this isn’t only you.
There’s a whole industry around trying to find out which sites rank for which cause and even the information we know is changing all the time.
We can’t provide a detailed explanation of how the Google algorithm works for you (no one can), but maybe we can provide some basic information about how search engines operate that could help to eliminate some of the mystery. Here are some of the key things you should hear about.
Search Engine Goals
The first thing to consider about how search engines work is that their priority is to provide the best possible results about what the user is searching about.
When it comes to natural results, the search engine is not worried about how much a specific website owner may want to capture those top spots or think you deserve them – they just care about people searching.
By delivering the information users need, a search engine will ensure that these users keep coming back to use the site again. We know how good it performed for Google because many of us use it every day.
That primary goal leads to the second goal that creates the company’s profits: making money on ads. Companies pay to advertise on search engines, this is a huge part because they know a large number of people use them daily. As long as Google keeps its users satisfied and coming back, advertisers will continue to keep the company profitable.
Indexing
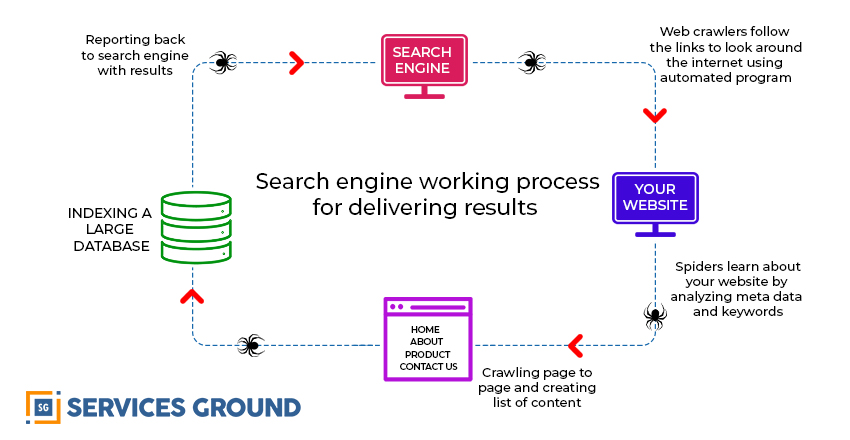
The index is where the pages you’ve found are kept. After a crawler finds a website, the search engine renders it much as a browser would. In doing so, the search engine analyses the contents of that page. All of this information is stored in the index.
This index attempts to identify and manage every website and web page on the web in such a way that it makes it possible to draw a link between the keywords people search for, and the content on each page.
Above all, it must be able to assign a standard of proportion to different web pages that cover the same topic.
It’s difficult because it’s all happening with machines. People spend a lot of time creating “quality” content, but search engines have to determine based on the factors that machines can reasonably measure.
Crawlers
The very first challenge to create a search engine database is to find all the web pages out there.
This part of the process is up to the web crawlers. Each time a web crawler finds a page, they crawl a page, collecting all the necessary information for the search engine index.
Search Engine Algorithms
The second challenge of the search engine index is more complex: attributing relative value to all of the web pages.
If a website crawler finds 100,000 pages that contain content that they deem relevant to a specific term, how will the search engine decide which order to submit those results?
This is where search engine algorithms come into play. Engineers at each of the major search engine companies have spent hours developing sophisticated algorithms. Which uses a number of factors to assign a ratio to websites and web pages.
Ranking Factors
Google and other search engines have provided some information about the ranking factors they use. But they are generally quite silent about how their search engine algorithms work.
They don’t want people trying to manipulate the results. – Something that has long been a problem with a black hat (SEO) practitioners.
Although there are many different factors that decide why one page ranks over another – we can discuss here, we have an idea of some of the most significant Google search engine ranking factors,
- Links
Links are the most important ranking factor, especially external links (those that point from one site to another) because whenever another website links to you, it indicates to Google that there is something authentic or valuable on this page that is being linked to.
- Website age
Older websites are generally considered more reliable and authentic than newer ones.
Search engines always try to provide as many relevant results as possible. So they look for terms on the search page related to the query of the person searching. The more relevant keywords you use, the more search engines indicate that your content is relevant.
- Mobile friendly
Google has been at the forefront of mobile usage as a ranking factor. If your website looks amazing on the desktop but has never been optimized for mobile use, it can hurt your rankings.
- Page speed
People are busy, and so are the search engines. Because of this, the slow-loading page would rank lower.
- Behavior data
Google looks at people when they reach the search engine results page (SERP). If someone clicks on a page and immediately backtracks – it indicates that the page does not provide what they were looking for. On the contrary, if they instead spend time on the page or even click on different pages on the site, it shows Google that the site is important.
Thanks for reading.
If you liked this article and want to read more of these, please subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on Facebook, Youtube, and Twitter.